
The Advantages of Collaborative Robots in Welding Applications
The Advantages of Collaborative Robots in Welding Applications
Collaborative robots, or "cobots," have emerged as transformative tools in industrial automation, particularly in welding—a field traditionally dominated by large, fixed industrial robots. By combining advanced sensing, user-friendly programming, and human-robot interaction capabilities, cobots address longstanding challenges in welding while unlocking new opportunities for flexibility, efficiency, and cost savings. Below, we explore the key advantages of deploying collaborative robots in welding processes.
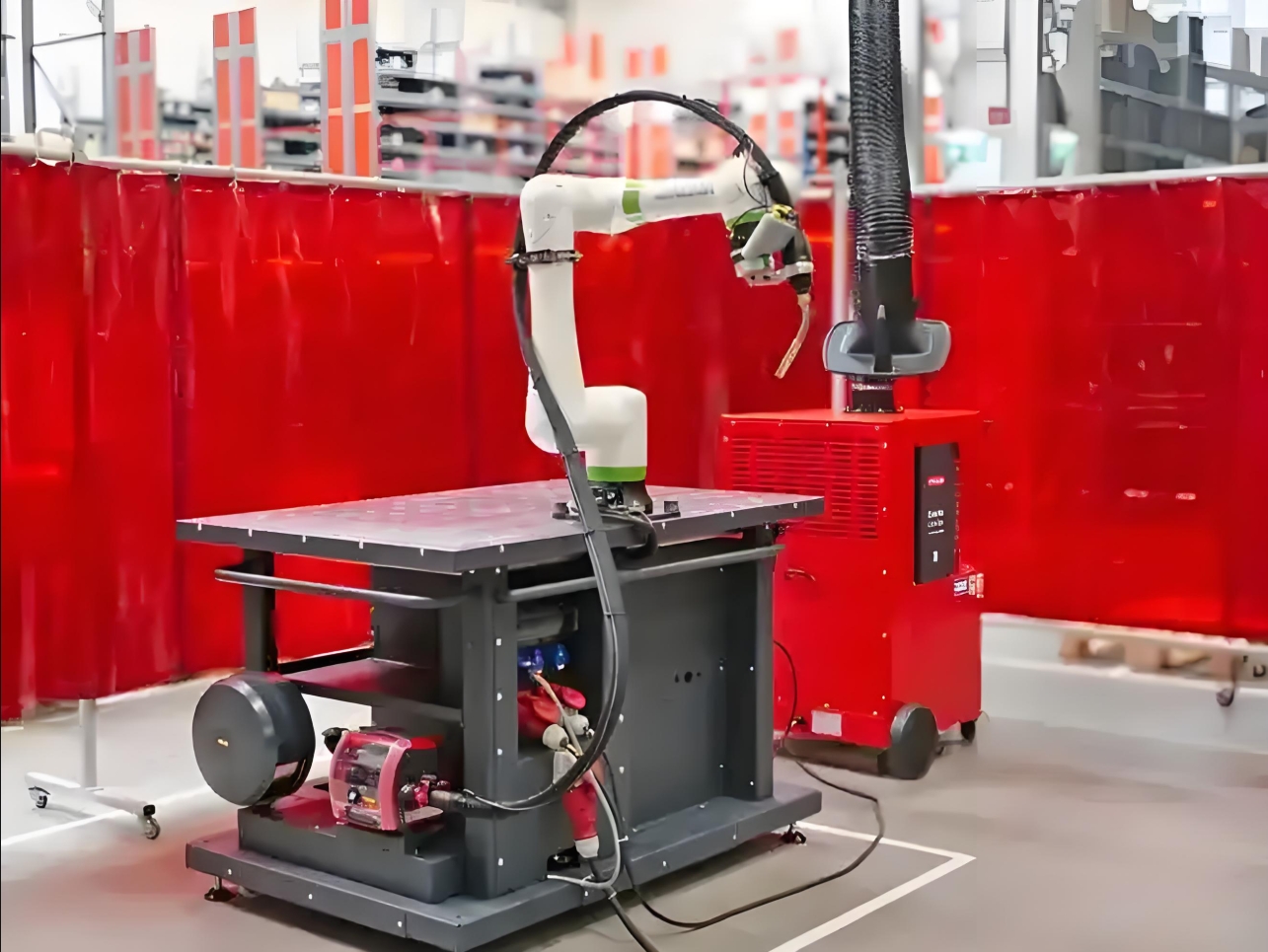

1. Enhanced Safety in Shared Workspaces
Safety is a cornerstone of collaborative robotics. Unlike conventional industrial robots, cobots are designed to operate alongside human workers without the need for bulky safety cages or extensive physical barriers. Equipped with force-limiting mechanisms, collision detection sensors, and real-time responsiveness, cobots can immediately halt or adjust their movements upon contact with humans or unexpected obstacles.
In welding environments, where sparks, heat, and hazardous fumes are common, this inherent safety feature minimizes risks to operators. For instance, a cobot can pause its welding torch if a worker enters a predefined safety zone, ensuring seamless collaboration without compromising productivity. This capability is especially valuable in small-batch or custom welding jobs, where human oversight and rapid adjustments are critical.
2. Flexibility for Small-Batch and High-Mix Production
Traditional welding robots excel in high-volume, repetitive tasks but struggle with frequent product changeovers. Cobots, however, are built for adaptability. Their lightweight design, easy mobility, and intuitive programming interfaces allow manufacturers to redeploy them across multiple welding stations or processes with minimal downtime.
For example, a cobot programmed for arc welding can be quickly reconfigured for spot welding or soldering by simply swapping end-effectors (e.g., welding torches) and updating software parameters. This flexibility is ideal for industries like automotive prototyping, aerospace, or custom metal fabrication, where low-volume, high-variability production is the norm. Additionally, cobots can handle irregularly shaped or delicate parts that might challenge rigid automation systems.
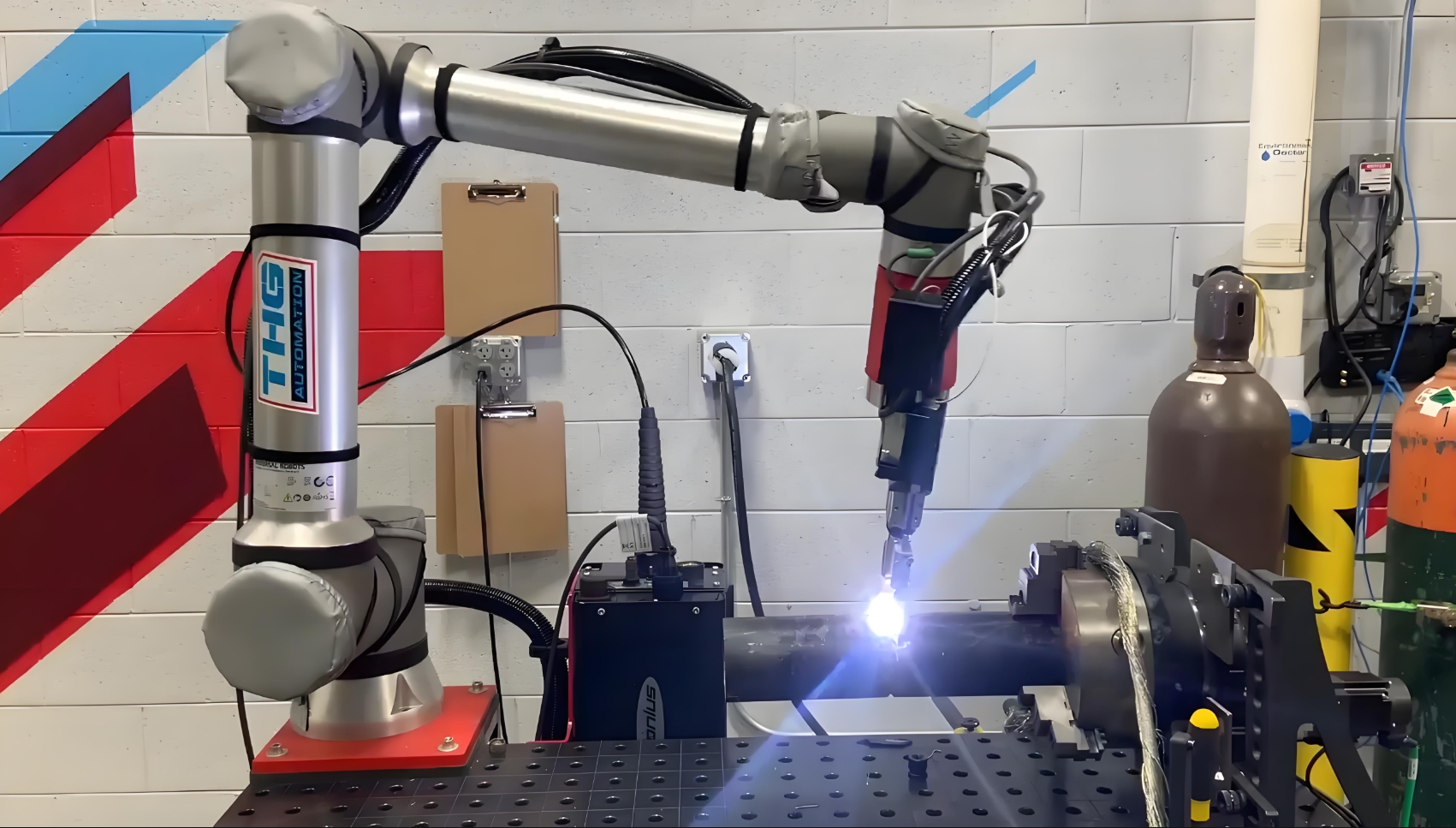
3. Lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Deploying traditional welding robots often requires significant upfront investments in hardware, safety infrastructure, and specialized personnel. Cobots, by contrast, offer a more cost-effective entry point into automation. Their compact size eliminates the need for extensive floor space modifications, while reduced safety barriers lower installation costs.
Moreover, cobots simplify programming. Using hand-guiding, teach pendants, or even graphical interfaces, operators with minimal robotics expertise can train cobots to perform welding paths. This reduces reliance on external automation engineers and shortens ROI timelines. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), cobots democratize access to precision welding automation without the financial burden of traditional systems.
4. Precision and Consistency in Weld Quality
Welding demands millimeter-level accuracy to ensure structural integrity and aesthetic quality. Cobots achieve this through advanced motion control systems and integrated vision technologies. Force-torque sensors enable cobots to maintain consistent contact pressure during arc welding, even on curved or uneven surfaces. Simultaneously, vision systems can scan workpieces to adjust welding paths in real time, compensating for part misalignment or thermal distortion.
This precision minimizes defects such as undercuts, porosity, or incomplete fusion, reducing rework rates and material waste. For industries like medical device manufacturing or electronics, where weld quality is non-negotiable, cobots deliver repeatable results that meet stringent regulatory standards.
5. Seamless Human-Robot Collaboration
Cobots thrive in hybrid workflows where humans and robots complement each other’s strengths. In welding applications, operators can focus on higher-level tasks—such as quality inspection, fixture setup, or complex joint alignment—while cobots handle repetitive or ergonomically challenging welding operations.
For instance, a worker might position a large, unwieldy metal component, while a cobot performs precise welds in tight spaces that would strain a human operator. This synergy boosts overall productivity and reduces physical fatigue, particularly in labor-intensive industries.
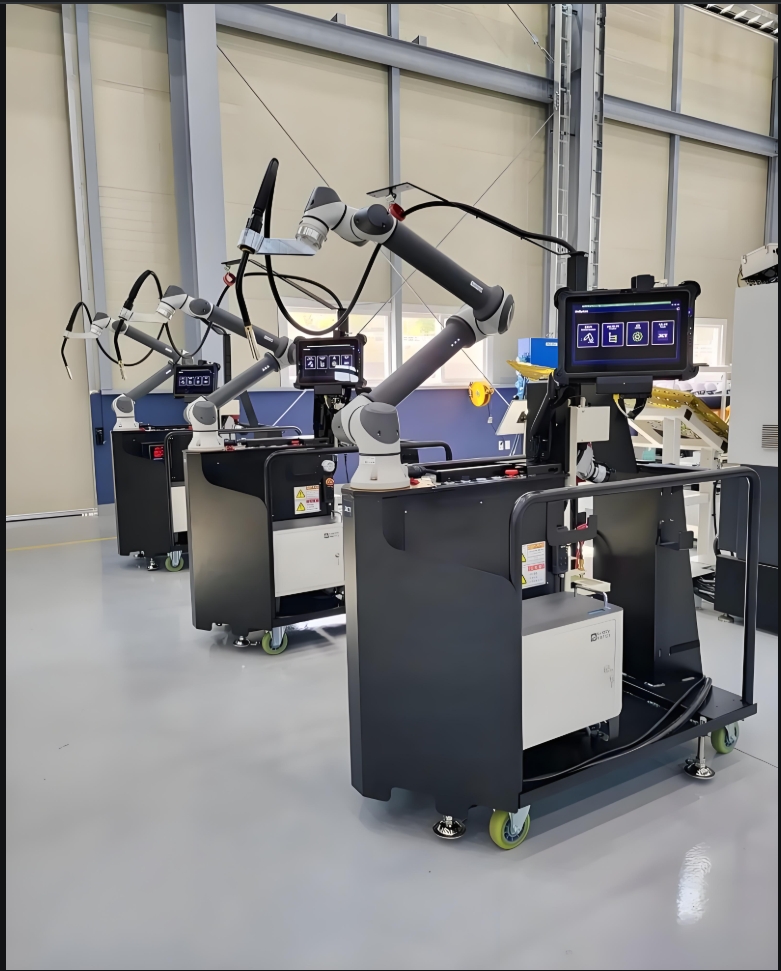

6. Rapid Deployment and Scalability
Traditional welding automation systems often require months of integration and calibration. Cobots, however, can be operational within hours. Pre-configured welding software packages (e.g., for MIG, TIG, or laser welding) and plug-and-play compatibility with common welding equipment accelerate setup.
This agility also supports scalability. Manufacturers can start with a single cobot for pilot projects and incrementally expand their fleets as demand grows. Such modularity is invaluable for businesses navigating fluctuating
7. Integration with Industry 4.0 and IoT
Modern cobots are designed for connectivity. Built-in IoT capabilities enable remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data collection (e.g., weld parameters, cycle times). This data can be analyzed to optimize welding processes, reduce energy consumption, or predict equipment failures before they occur.
Furthermore, cobots can interface with other smart factory components, such as automated material handling systems or digital twin platforms, creating a cohesive, data-driven production ecosystem.
Conclusion
Collaborative robots are redefining welding by merging the precision of automation with the adaptability of human labor. Their safety features, flexibility, and cost efficiency make them ideal for SMEs and large enterprises alike, particularly in industries prioritizing customization, rapid prototyping, or lean manufacturing. As welding technologies evolve—such as advancements in laser welding or additive manufacturing—cobots will remain at the forefront, enabling manufacturers to stay competitive in an era of dynamic market demands.
By adopting cobots for welding, companies not only enhance productivity and quality but also future-proof their operations, ensuring they are ready to embrace the next wave of industrial innovation.
Weldingcobot,,Collabotrative,welding,robot,JOCRT,,UR
previous page
next page




